第七屆泛太平洋生殖醫學會北醫生殖醫學中心及合作醫學機構共有四篇得獎論文
貼出以饗大家
HYPOXIA STRESS ENHANCES THE IGF-1 SIGNALING IN PLURIPOTENT MOUSE GERMLINE STEM CELLS
HYPOXIA STRESS ENHANCES THE IGF-1 SIGNALING IN PLURIPOTENT MOUSE GERMLINE STEM CELLS
Yi-Chun Chen1,2, Hsu-Liang Chiang1,2, Shu-Fen Cheng2, Thai-Yen Ling4, Yen-Hua Huang1,2,3, Chii-Ruey Tzeng3
1 Department of Biochemistry, MedicineTaipei Medical University Hospital (Taiwan)
2 Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, MedicineTaipei Medical University Hospital (Taiwan)
3 Center for Reproductive, MedicineTaipei Medical University Hospital (Taiwan)
4 Institute of Pharmacology,College of Medicine, National Taiwan University (Taiwan)
Recent advances in cancer research suggest that existance of cancer stem cells (CSCs) in tumor tissues. The origin of
CSCs are still controversial; but it has been proved CSCs are possibly originated from organ stem cells (e.q. glioma CSCs
and intestine CSCs). The niche stress such as hypoxia effect may provide external signals in stem cell transformation.
However, the mechanism of hypoxia-induced stem cell transformation still remains unclear. Our preliminary observations in
human pluripotent testicular tumors (seminomas and embryonal carcinomas) showed a high level of hypoxia-inducible
protein HIF-1α/HIF-2α as well as IGF protein expression in tissues. This observation strongly highlights the cross-talking of
niche hypoxic stress and IGF-1 signaling in transformation of germline stem cells into pluripotent cancers. To address this
point, we have successfully established a serum-free stem-niche cell co-culture system to generate pluripotent germline
stem cells from neonatal mouse testis (AP+GSCs), and uncovered the role of IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling in germ cell
pluripotency. Interestingly, while comparing with the normoxia ( 21 % O2), the AP+GSCs showed in a dramatically increase
of alkaline phosphatase activity (AP), cell proliferation, HIF-1α, HIF-2α, Oct-4 protein expression, and pluripotent gene
expression (such as Oct-4, Sox2, Nanog, Klf-4, and c-Myc) under hypoxia condition (5 % O2). Moreover, the IGF-1 and
IGF-1R expression were also significantly increased under hypoxia. Further analysis by using PPP (a specific inhibitor of
IGF-1R phosphorylation) and/or LY294002 (a specific PI3K inhibitor) treatment dramatically reduced the Oct-4 expression
as well as HIF-1 /HIF-2 ?protein of AP+GSCs. These results highlight the regulation of Oct-4/HIF-2α expression by
IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling. In summary, our results demonstrated an up-stream regulation of stemness (Oct-4, Sox2, Nanog,
and Klf-4) and tumor factor (c-Myc) of AP+GSCs which was cross-talking with IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling in stem cell
transformation under hypoxia condition.
K
ㄒ

ROLE OF IGF-1 / IGF-1R SIGNALING IN MOUSE GERMLINE STEM CELLS’ PLURIPOTENCY AND TUMORIGENESIS
Shu-Fen Cheng1,2, Jun-Jen Liu4, Chii-Ruey Tzeng3, Yu-Chieh Lee2,4, Cheng-Chieh Chin1,2, Thai-Yen Ling5, Yen-Hua
Huang1,2,3,
1 Department of Biochemistry,Taipei Medical University (Taiwan)
2 Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, School of Medicine (Taiwan)
3 Center for Reproductive Medicine, Taipei Medical University Hospital, Taipei Medical University (Taiwan)
4 School of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology, Taipei Medical University (Taiwan)
5 Institute of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University (Taiwan)
Stem cell niche is known to affect cell fate critically, especially for self-renewal and differentiation. Germ line stem cells
(GSCs) are cells which are able to self-renew and differentiate into mature sperms and are known to be pluripotent for their
in-vivo ability in teratoma formation. Recent advances in cancer research suggest that there exist cancer stem cells (CSCs
in tumors. The resources of CSCs are unclear. Originality of CSCs from its stem cells have been hypothesized (like glioma
CSCs and intestine CSCs). However, mechanisms which regulated the transformation of GSCs into CSCs still remain
unclear. The niche stress such as inflammation may provide external signals in stem cell transformation. Our preliminary
observations in human pluripotent testicular tumors (seminomas and embryonal carcinomas) have found the high
expression of inflammatory proteins (CD68 macrophage and chemokine MCP-1) as well as IGF-1/IGF-1R protein in
tissues.This observation strongly highlights the cross-talking of niche inflammation and IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling in
formation of germline CSCs. To address this point, in this thesis, we have successfully established a serum-free
stem-niche cell co-culture system to generate pluripotent GSCs from neonatal mouse testis (AP+GSCs). Further
experiments have demonstrated the role of IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling in germ cell pluripotency. Interestingly, by utilizing an in
vitro inflammation model, we found the AP+GSCs showed in high proliferation rate, and expressed strong AP activity and
pluripotency-associated gene (such as Oct-4 and Nanog). Moreover, by using slot blot, we also detected a significant
increasing of IGF-1 level in medium which is secreted by Leydig cells and myoid cells. In summary, in this study, we
presented a serum-free testicular stem-niche cell co-culture system to demonstrate the inflammation effect on AP+GSCs’
pluripotency and tumorigenesis; and, such regulation mechanisms may through IGF-1/IGF-1R-mediated PI3K/Akt
signaling. This finding may provide clinical values in tumor therapy of human testicular germ cell tumors.

RECONSTITUTION OF SPERMATOGENESIS FROM TESTIS FAILURE AFTER SPERMATOGONIAL STEM CELLS
(SSC) TRANSPLANTATION FOR MALE FERTILITY PRESERVATION-A TRANSGENIC MOUSE MODEL
Chi-Huang Chen1, Wei-Jen Shang1, Shun-Jen Tan1, Gwo-Jang Wu1, Jah-Yao Liu1, Chii-Ruei Tzeng2, Chi-Huang Chen2,
Yung-Chieh Tsai3
1 National Defense Medical Center (Taiwan)
2 Graduate Institute of Clinical Medicine, Taipei Medical University (Taiwan)
3 Center for Reproductive Medicine, Chi Mei Medical Center (Taiwan)
Purpose: Fertility preservation for prepubertal male mouse is feasible by the reconstruction of spermatogenesis after
spermatogonial stem cells transplantation.
Materials and methods: A. Donor cell preparation. Cells for transplantation are obtained from testes of FVB/N-Tg (PolII-luc)
Ltc transgenic mouse 5 to 60 days after birth by a two-step enzymatic digestion protocol. The cell volume needed to inject
both testes of a mouse ranges from 0,1 to 0,5 ml depending on the injection method. Cell concentrations of up to about
300xl06 cells per ml can be used. Concentrations above 106 cells/ml are associated with high levels of clumping and
plugging of pipettes, which may be reduced by the addition of DNAse at the time of injection. The cells are maintained at
SSC until the time of loading into an injection pipette, usually 1 to 4 h. B. Transplantation of SSC into recipient mouse. In
this prcedure, donor cells are harvested from the testes of fertile donor mice that express a reporter transgene, and
suspension of the cells are microinjected into seminiferous tubules of FVB/NJNarl wild type recipient infertile adult mice at
6-week-old after complete busulfan-induced testis failure. C. In vivo tracking of grafted SSC by bioluminescence imaging
(BLI). Reporter genes can be used to assay for the activity of a particular RNA Polymerase II promoter (PolII) in each
viable cell. Reporter gene products are luciferase (enzymes). The enzyme luciferase catalyzes a reaction with a luciferin to
produce light which is quantified as quantum. The reporter gene is simply placed under the control of the target promoter
(PolII) and the reporter gene product's activity is quantitatively measured. After gonadal tissues or germ cells
transplantation, each mouse was imaged every other day for 2 weeks and subsequent every weeks for 2 months. For
imaging of mice with gonadal tissue transplants. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane. A saturating concentration of the
substrate D-luciferin was injected intraperitoneally (150 mg/kg). Bioluminescence was quantified the quantum by summing
pixel intensities within equal area ROI. D. Fertilization assay. Mating the recipient male to a wild-type female, then progeny
is produced by nature fertility.
Results: Live birth pup of FVB/N-Tg (PolII-luc) Ltc transgenic mouse were born and imaged by bioluminescence after
mating FVB/NJNarl female wild type and male wild type recipient 3-4 month after FVB/N-Tg (PolII-luc) SSC
transplantation.
Conclusions: Spermatogonial stem cell transplantation could be used to restore fertility in men following chemotherapy or
radiation treatment. Development of techniques for the in vitro differentiation of spermatogonial stem cells to functional
spermatozoa is a crucial step for the treatment of infertility or germline gene therapy






A NEW SERUM MARKER FOR ENDOMETRIOSIS
Shih-En Yi1, Shui-Tsung Chen1, Andrew H-J Wang1, Wei-Chung Vivian Yan2, Shih-En Yi2, Hsiao-Ling Wang2, Chii-Ruey
Tzeng3
1 Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica (Taiwan)
2 Graduate Institute of Biomedical Materials & Engineering, Taipei Medical University (Taiwan)
3 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Taipei Medical University Hospital (Taiwan)
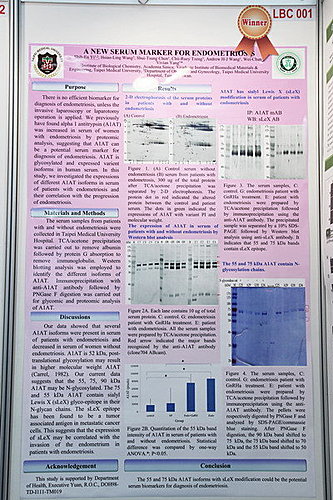
Purpose: There is no efficient biomarker for diagnosis, unless the invasive laparoscopy or laparotomy operation is applied
to confirm the occurrence of endometriosis. We previously have found alpha 1 antitrypsin (A1AT) was increased in serum
of women with endometriosis by proteomic analysis, suggesting that A1AT can be a potential serum marker for diagnosis
of endometriosis. A1AT is glycosylated and expressed as variant isoforms in human serum. In this study, we investigated
the expressions of different A1AT isoforms in serum of patients with endometriosis.
Materials and methods: The serum samples from patients with and without endometriosis were collected in Taipei Medical
University Hospital. TCA/acetone precipitation was carried out to remove albumin followed by protein G absorption to
remove immunoglobulin. Western blotting analysis was employed to identify the different isoforms of A1AT.
Immunoprecipitation with anti-A1AT antibody followed by PNGase F digestion was carried out for glycomic and proteomic
analysis of A1AT.
Results: Western blotting data showed that 55, 65, 70 and 90 kDa bends were detected by the anti-A1AT antibody. The 55
and 70 kDa A1AT were significantly present in patients with endometriosis compared to that in women without
endometriosis. The 55 and 90 kDa forms were N-glycosylated. Additionally, sialyl Lewis X glyco-epitope was expressed
significantly in serum of patients with endometriosis.
Conclusion: The 55 and 70 kDa A1AT isoforms and the sLeX modification of A1AT could be the potential biomarkers for
diagnosis of endometriosis.